Higher Performance Insights | LEADER INSIGHTS: SUMMER SEMESTER "HOW TO" SPECIAL EDITION
Real HOW TO solutions from real educational leaders---and the research-backed answers that can transform how you navigate the complexities of modern leadership
When 62% of senior leadership teams report significant gaps in psychological safety---the very foundation they're supposed to create for others---we have a leadership crisis hiding in plain sight.
Every semester, I receive hundreds of questions from district and campus leaders through our executive coaching exchanges. These conversations occur in confidence — during leadership intensives, one-on-one coaching sessions, and late-night calls when the weight of responsibility feels overwhelming.
This summer semester, I decided to pull some of the most compelling questions and share my thoughts publicly, restructuring them using the innovative "HOW TO" approach pioneered by Bradley Fuster and San Francisco Bay University. Their brilliant transformation of traditional course titles—eliminating the yawn-inducing "English 101" or "Intro to Marketing" in favor of practical "HOW TO" titles—has revolutionized how students engage with learning.
We're applying that same energy to leadership challenges. These aren't hypothetical scenarios — they're real challenges from real leaders in districts and on campuses across the country. Names have been changed for confidentiality, but the struggles are authentic. If you find this format helpful, let me know. We plan to make this a special semester edition going forward.
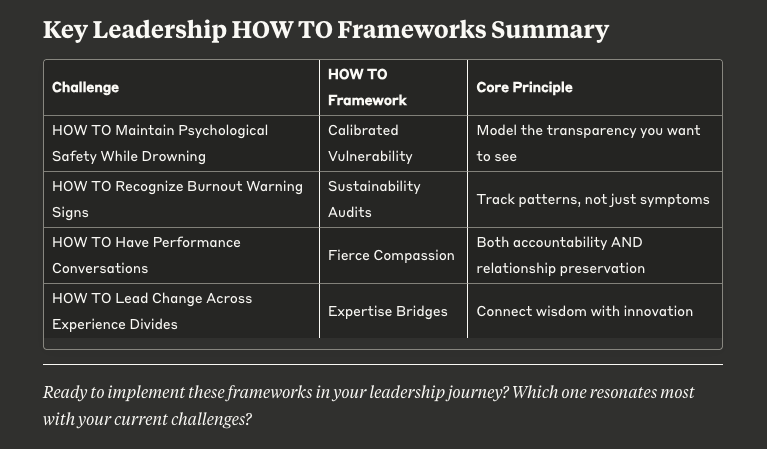
HOW TO: Maintain Psychological Safety for Your Team When You Feel Like You're Drowning
Original question: "How do you maintain psychological safety for your team when you yourself feel like you're drowning? I'm supposed to be the calm, confident leader, but inside I'm struggling with imposter syndrome and the constant pressure to have all the answers." - Maria, University Vice President for Academic Affairs
Maria, you've hit on the central paradox of every modern leader of people and systems: You can't give what you don't have, yet your role systematically strips away the very conditions you need to create for others.
Recent research, tracking 769 K-12 staff members over four years, revealed predictable patterns in educational psychological safety. While 51% maintained stable-high levels and 44.8% remained at stable-medium, 4.2% experienced dynamic-low psychological safety. But here's what the research doesn't capture: Leaders often exist in a separate category entirely, experiencing what I call "psychological safety deficit disorder."
The stakes become even higher when we examine senior leadership dynamics specifically. Studies of nearly 300 leaders over 2.5 years found that teams with high degrees of psychological safety reported higher levels of performance and lower levels of interpersonal conflict. For senior leadership teams, where research found members reported the greatest differences in their perceived levels of psychological safety, 62% of senior teams demonstrated significant variability.
The Calibrated Vulnerability Solution
Maria, here's what you need to understand: Your imposter syndrome isn't a personal failing---it's an occupational hazard. When you're constantly in "performance mode," authentic connection becomes impossible. But psychological safety isn't built through perfection; it's built through what I call "calibrated vulnerability."
Start with one person — your most trusted team member — and practice transparent leadership. "I'm working through this challenge and here's my thinking..." This isn't weakness; it's modeling the very behavior you want to see in your organization.
The psychological safety you create for others begins with the psychological safety you create for yourself. When you demonstrate that uncertainty is acceptable, that thinking out loud is valuable, and that perfection isn't the standard, you give your team permission to do the same.
Understanding psychological safety challenges leads us naturally to the next critical area: recognizing when those challenges are pushing leaders and teams toward burnout.
HOW TO: Recognize Early Warning Signs of Burnout (That 90% of Leaders Miss) in Yourself and Your Team
Original question: "What early warning signs should I watch for in myself and my team to prevent burnout before it becomes a crisis? I've seen too many good people leave education because they reach their breaking point." - Robert, Superintendent of Schools
Robert, you're asking the right question at exactly the right time. A comprehensive meta-analysis of 348 studies involving over 3.6 million participants found that educational leadership impact on student achievement diminished significantly during exceptional circumstances like the COVID-19 pandemic---and burnout is often the culprit.
The early warning signs aren't what most leaders think. It's not the obvious exhaustion or irritability. It's the subtle shifts that happen weeks before the crash:
Individual Level Warning Signs:
- Decision fatigue masquerading as perfectionism
- Emotional numbing disguised as "professional boundaries"
- Innovation paralysis---when everything feels like a risk
Team Level Warning Signs:
- Decreased psychological safety, which research shows is consistently associated with greater perceived supports and lower burnout
- Communication becoming transactional rather than relational
- Loss of collective problem-solving capacity
System Level Warning Signs:
- Increased reliance on formal authority instead of influence
- Policy creation as a substitute for leadership presence
- Meeting multiplication- when committee work becomes the primary communication strategy
The Sustainability Audit Framework
The intervention framework I use with leaders: Implement what I call "sustainability audits" monthly. Ask your team: "What's one thing that's energizing you right now? What's one thing that's draining you?" Track patterns, not just individual responses.
When you catch burnout in its early stages — before the obvious symptoms appear — you can address the root causes rather than managing crisis symptoms.
Preventing burnout requires honest assessment, but it also demands the courage to have difficult conversations when performance issues arise. This brings us to one of leadership's most delicate challenges.
HOW TO: Have Tough Conversations with Star Faculty Who Aren't Performing Without Losing Their Institutional Knowledge
Original question: "How do you have tough conversations with long-term faculty members who aren't performing but have institutional knowledge you can't afford to lose? I feel stuck between accountability and preservation of relationships." - Jennifer, College President
Jennifer, you've identified what researchers call "the competence-commitment paradox"-when emotional investment in people conflicts with organizational performance needs. Recent research on school leadership during crises has found that democratic, humanistic, and participatory leadership styles are most effective in maintaining mental health and performance; however, these approaches require skilled navigation of exactly this tension.
The mistake most leaders make is treating this as an either/or choice: accountability OR relationship preservation. High-performing institutions understand it's a both/and challenge that requires what I've developed as the "fierce compassion framework" — a both/and approach that honors relationships while driving results.
The Fierce Compassion Framework:
Step 1 - Separate the person from the performance. Start the conversation with: "I value you and your contributions to this institution. That's exactly why we need to address this performance gap."
Step 2 - Make the institutional knowledge visible. "Your understanding of our campus culture and history is invaluable. I want to find ways to leverage that while also ensuring you're set up for success in your current role."
Step 3 - Create a growth pathway, not a correction plan. Research indicates that individuals respond more positively to development opportunities than to performance improvement plans. Focus on building capacity, not just addressing deficits.
Step 4 - Set clear timelines with support systems. "Here's what success looks like, here's how I'll support you, and here's our timeline for seeing progress."
Having the conversation IS preserving the relationship, not destroying it. Avoiding it destroys both the relationship and the performance.
Even when we master difficult one-on-one conversations, we still face the broader challenge of leading change across diverse groups with varying levels of experience and buy-in.
HOW TO: Lead Change When Your Most Experienced Faculty Resist While Your Newer Leaders Lack Credibility
Original question: "How do you lead change when your most experienced faculty resist new initiatives, but your newer department chairs lack the credibility to drive implementation? I feel caught between generational divides." - David, University Vice President for Strategic Initiatives
David, you're dealing with what recent leadership research identifies as the distributed leadership challenge — how to harness collective intelligence while managing natural resistance to change. This isn't actually about generational divides; it's about recognizing expertise and changing ownership.
Studies on distributed leadership show that transformative change happens when leadership becomes "a collective endeavor involving multiple stakeholders" rather than top-down mandate implementation. The key is creating what I call "expertise bridges."
The Expertise Bridge Strategy:
Phase 1 - Map the real expertise. Your experienced staff have implementation wisdom; your newer staff have innovation energy. Neither group has complete expertise — and that's your advantage.
Phase 2 - Create mixed-expertise teams. Pair your most experienced faculty with your most innovative department leaders. Give them shared ownership of both the problem definition and solution design.
Phase 3 - Use resistance as data. When experienced faculty resist, they're often identifying implementation challenges that enthusiastic newcomers miss. Reframe resistance: "What implementation challenges is this concern highlighting?"
Phase 4 - Build credibility through collaboration. Let your newer department chairs gain credibility by successfully partnering with respected faculty veterans, not by challenging them.
The breakthrough happens when both groups realize they need each other to succeed. Your job isn't to choose sides — it's to orchestrate that realization.
The Hidden Factor Behind Breakthrough Teams
Here's what I've learned from working with hundreds of educational leadership teams: The difference between leaders who thrive despite challenges and those who get overwhelmed isn't individual resilience — it's about Team Intelligence (TQ).
When teams develop high Team Intelligence, they naturally create the psychological safety cues that prevent burnout and amplify collective problem-solving. They learn to respond to the isolation of leadership, just as the most effective educational systems do—by building sustainable support networks rather than relying on heroic individual effort.
The TQ Advantage for Educational Leaders:
- 48% faster recovery from leadership challenges
- 42% higher staff retention and engagement
- 39% more innovative solutions to complex educational problems
The breakthrough teams I work with understand that educational leadership doesn't have to be a solo endeavor. When teams develop Team Intelligence, mutual support becomes their natural response to pressure.
These four leadership challenges — psychological safety deficits, burnout prevention, difficult performance conversations, and change resistance — represent the core struggles that every educational leader faces. However, they also represent the greatest opportunities for building Team Intelligence, which transforms individual challenges into a collective problem-solving capacity.
Ready to Transform Leadership Challenges into Team Strength?
Stop trying to handle the complexity of educational leadership on your own. Start building the Team Intelligence that transforms individual challenges into collective problem-solving capacity.
The first step is understanding your team's current Team Intelligence. In just 5 minutes per team member, you can discover:
- Where leadership isolation is most likely to impact your team's performance
- Which team dynamics naturally create psychological safety for leaders
- How to transform the toughest leadership challenges into team development opportunities
https://www.higherperformancegroup.com/team-intelligence-assessment
Discover Your Team Intelligence → https://www.higherperformancegroup.com/team-intelligence-assessment
Because when you can't create sustainability among leaders, you can't create results for students. But when you develop Team Intelligence, the challenges that overwhelm individual leaders become the problems that strengthen entire teams.
Just as educational leaders have learned to leverage collective intelligence, you can too, starting today.
Special thanks to San Francisco Bay University for modeling the transformative "HOW TO" approach to course titles and learning engagement. Their innovation in eliminating traditional academic jargon in favor of practical, action-oriented titles has inspired educational institutions nationwide to rethink how they present learning opportunities.
Want More Battle-Tested Leadership Tools?
Find this article with bonus material at higherperformancegroup.com/blog, including Leader {CORE} Leader Guides for leading timely discussions on this topic and dozens more with proven strategies to transform teams.
Be the First to Know: Join Our Mailing List! Get Higher Performance Insights in your inbox and keep learning to lead Higher Performance Teams and Systems.
References
- Dickson, E., Lardier, D. T., Verdezoto, C. S., & Hackett, J. M. (2024). Reducing isolation for educators through ECHO virtual communities of practice. Frontiers in Education, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2024.1409721
- Edmondson, A. (1999). Psychological safety and learning behavior in work teams. Administrative Science Quarterly, 44(2), 350-383.
- Ertem, H. Y. (2024). School leadership fostering mental health in the times of crisis: synthesis of school principals' views and PISA 2022. BMC Psychology, 12(1), 695.
- Fleming, C. B., et al. (2024). Psychological safety among K‐12 educators: Patterns over time, and associations with staff well‐being and organizational context. Psychology in the Schools, 61(2), 476-495.
- Karadağ, E., & Sertel, G. (2025). The effect of educational leadership on students' achievement: A cross-cultural meta-analysis research on studies between 2006 and 2024. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 53(1), 142-167.
- Peng, T., Wang, C., Xu, J., Dai, J., & Yu, T. (2024). Evolution and current research status of educational leadership theory: A content analysis-based study. SAGE Open, 14(3).
- Zhang, H., et al. (2024). Distributed leadership in educational contexts: A catalyst for school improvement. Social Sciences & Humanities Open, 9, 100835.
Higher Performance Group helps campus leaders transform highly talented but average-performing teams into breakthrough leadership systems powered by Team Intelligence. Because individual brilliance is the ceiling, Team Intelligence is the breakthrough.
Short on quality leadership material for your team meetings?
Explore the vault of leadership topics and leader guides by joining The GROUP JOIN THE GROUP
Do you want more leadership topics and guides?
Join THE GROUP
An online community for higher education leaders, where we offer a library of lessons and guides that can be utilized during your leadership sessions and other resources.
Help Spread the Word
If you found value in this post, we’d love your help spreading the word! Please consider sharing this on your favorite social media platform and tag Higher Performance Group and Dr. Joe Hill. Your support helps us reach and inspire more awesome people like you!
Like What You've Read?
Get practical, research-based ideas to Accelerate
Higher Team Performance delivered straight to your inbox every Tuesday.
More Blog Articles





